Overall, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the average life of a fuse, emphasizing its significance in maintaining electrical safety and the reliable operation of electrical systems. We will explore the typical lifespan range for each type and examine the factors that contribute to the differences in fuse lifespan. Additionally, the quality of the fuse materials and manufacturing processes can also affect its longevity.
Table of Contents
A fuse serves as a safeguarding component inserted into an electrical circuit. It comes in various forms like cartridge fuses, blade fuses, and resettable fuses. Its main function is to detect and react to abnormally high currents. In the event of a surge, the fuse is intentionally designed to melt or blow out, effectively breaking the circuit and cutting off the electrical power supply. This protective action prevents excessive currents from harming the connected devices and significantly lowers the chances of electrical fires.
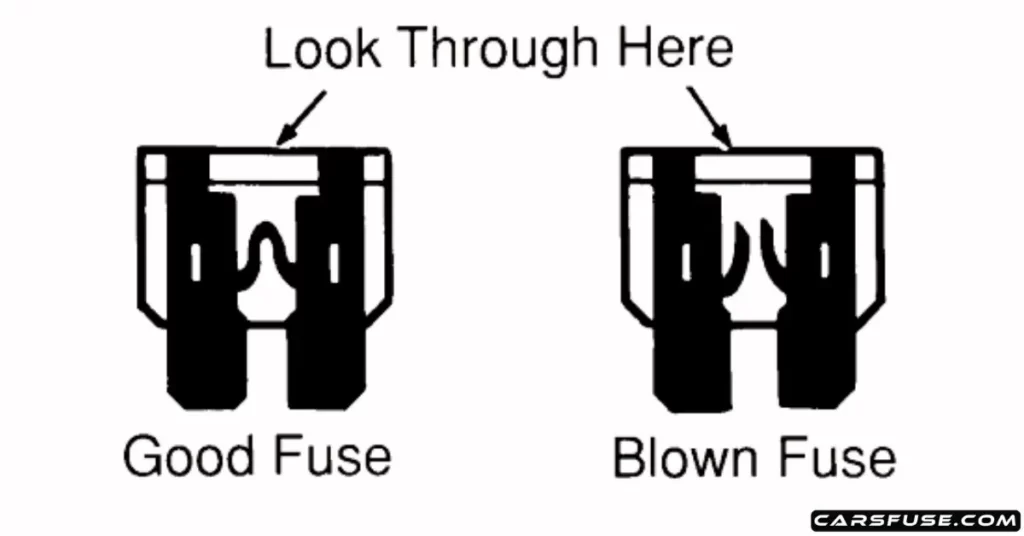
What are the factors affecting fuse lifespan?
1. Current rating and load capacity
The existing capacity of a fuse signifies the highest level of electric current it can safely manage. Continuous exposure to currents beyond its capacity can result in overheating and premature malfunctioning of the fuse. In a similar vein, surpassing the circuit’s load limit, which represents the amount of current passing through, can place excessive strain on the fuse and affect its longevity.
2. Ambient temperature and environmental conditions
The temperature surrounding a fuse plays a crucial role in its performance and longevity. Fuses are typically designed to operate within a specified temperature range. If the ambient temperature exceeds the fuse’s tolerance level, it can affect its ability to dissipate heat effectively and result in a shorter lifespan. Additionally, environmental conditions such as humidity, dust, and corrosive substances can also impact the fuse’s performance and lifespan.
3. Frequency and magnitude of electrical surges
Sudden and temporary rises in voltage or current, known as electrical surges, can greatly affect how long a fuse lasts. When a fuse is exposed to surges often or repeatedly, it can become strained and tired, making it wear out faster. Likewise, if the surges are too strong for the fuse to handle, it can cause the fuse to fail before its time.
4. Quality of fuse materials and manufacturing
The durability of a fuse is heavily dependent on the choice of materials during its construction and the manufacturing techniques applied. Fuses crafted with superior-quality materials and manufactured following rigorous standards are more likely to possess an extended lifespan compared to those constructed with inferior components. Various factors, including the composition of fuse elements, the design of the fuse casing, and the reliability of the manufacturing processes, collectively contribute to the overall excellence and robustness of the fuse.
Explore Hyundai Nexo Fuse Box Diagram Here!
What is the lifespan of different fuse types?
Different types of fuses, such as cartridge fuses, blade fuses, and resettable fuses, have varying average lifespans. By understanding the typical lifespan of each type, individuals can choose fuses that align with the specific application requirements. It is important to consider factors such as current rating, load capacity, and environmental conditions when selecting fuses to optimize their performance and longevity.
Cartridge fuses: They are designed to handle high currents and have a relatively long average lifespan commonly found in older electrical systems.
Blade fuses: They are widely used in modern vehicles have a more compact design and are relatively easier to replace. The average lifespan of blade fuses is typically shorter compared to cartridge fuses which may last anywhere from a few months to a couple of years.
Resettable fuses: These fuses are designed to handle low to moderate currents and are often used in electronic devices and circuit protection applications. Unlike cartridge and blade fuses, resettable fuses can automatically restore their functionality after a fault condition is resolved. The average lifespan of resettable fuses varies and depends on factors such as the number of times they are tripped, the magnitude of fault currents, and their overall quality.
For more information on troubleshooting car electrical issues, you can refer to our other related articles of the car fuses which provides in-depth information on common causes of fuse failures and offers effective solutions. Enhance your understanding of car electrical systems and address fuse-related challenges with confidence. Please do check through the link below: What causes car fuses to go bad? Can I replace a car fuse by myself? Do you need to disconnect battery to change fuse? How do I know if my car fuse box is bad or broken?
The final answer to your question what is the average life of a car fuse?
In conclusion, determining the average life of a fuse involves statistical analysis, testing methods, and adherence to industry standards. By considering factors such as current rating, load capacity, temperature, and surges, individuals can make informed decisions about fuse selection and maintenance. Periodic checks for signs of damage, wear, or overheating allow for prompt replacement of faulty fuses, reducing the risk of electrical failures.
Mitigating electrical issues, such as voltage spikes or overloaded circuits, also contributes to extending fuse lifespan. By doing so, individuals can ensure optimal fuse performance, minimize the risk of equipment damage, and maintain a safe electrical environment.
Tom Smith is a passionate car mechanic and automotive enthusiast, specializing in the intricate world of car fuse boxes. With years of hands-on experience under the hood, he has earned a reputation as a reliable expert in his field. As the founder and content creator of the popular blog website 'carsfuse.com,' Tom has dedicated himself to sharing his extensive knowledge of car fuse boxes and electrical systems with the world.

