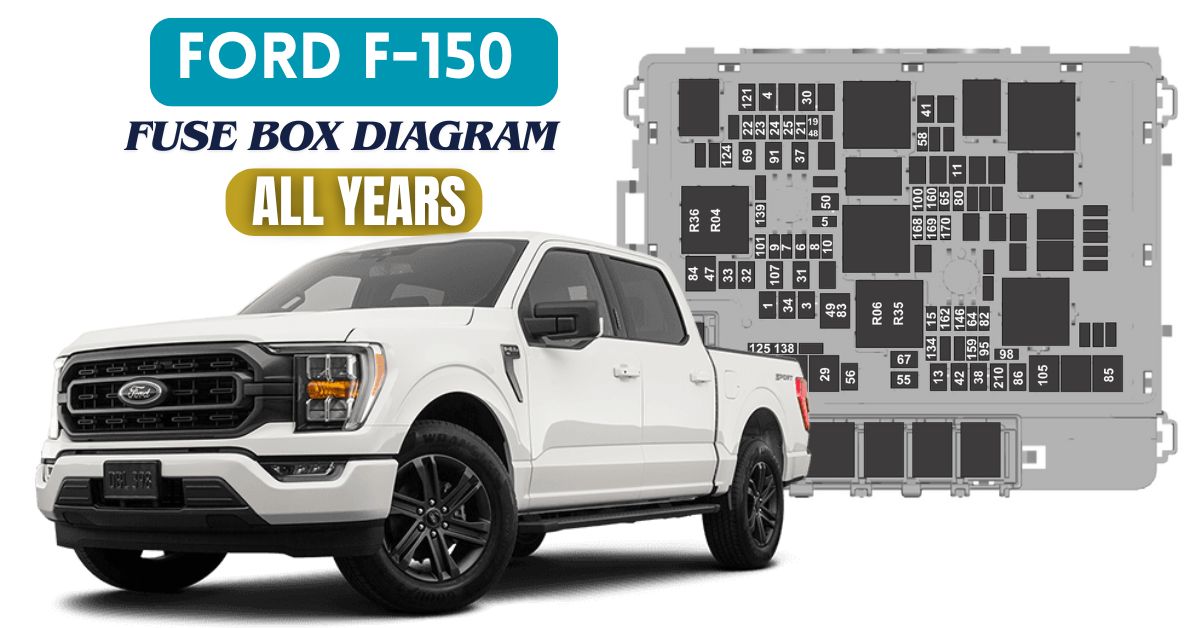
The Ford F-150 has been America’s best-selling truck for decades, offering reliability, power, and versatility. But like any vehicle, electrical issues can occur over time — and when they do, the fuse box is one of the first places to check.
Whether you’re troubleshooting a blown fuse, looking for the location of a specific relay, or performing DIY repairs, understanding the F-150’s fuse box diagram is essential.
In this complete guide, we’ll walk through Ford F-150 fuse box diagrams for all model years, explain their locations, and help you identify common fuse functions — from headlights and power windows to the fuel pump and horn.
Table of Contents
Why Fuse Boxes Matter in the Ford F-150
Your F-150’s electrical system is protected by a series of fuses and relays. Each fuse controls a specific circuit — such as your radio, headlights, or A/C — and prevents electrical overloads that could damage components or wiring.
If something stops working suddenly, like your horn or wipers, checking the corresponding fuse should be your first step. Replacing a blown fuse is often a quick and inexpensive fix.
Fuse Box Locations in the Ford F-150
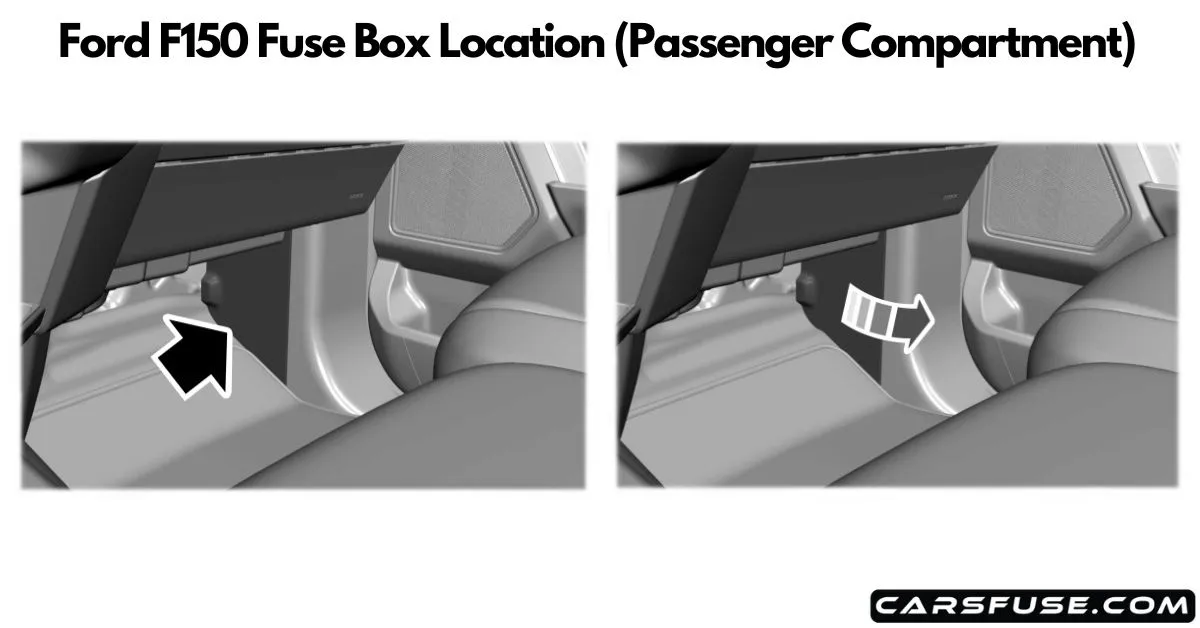
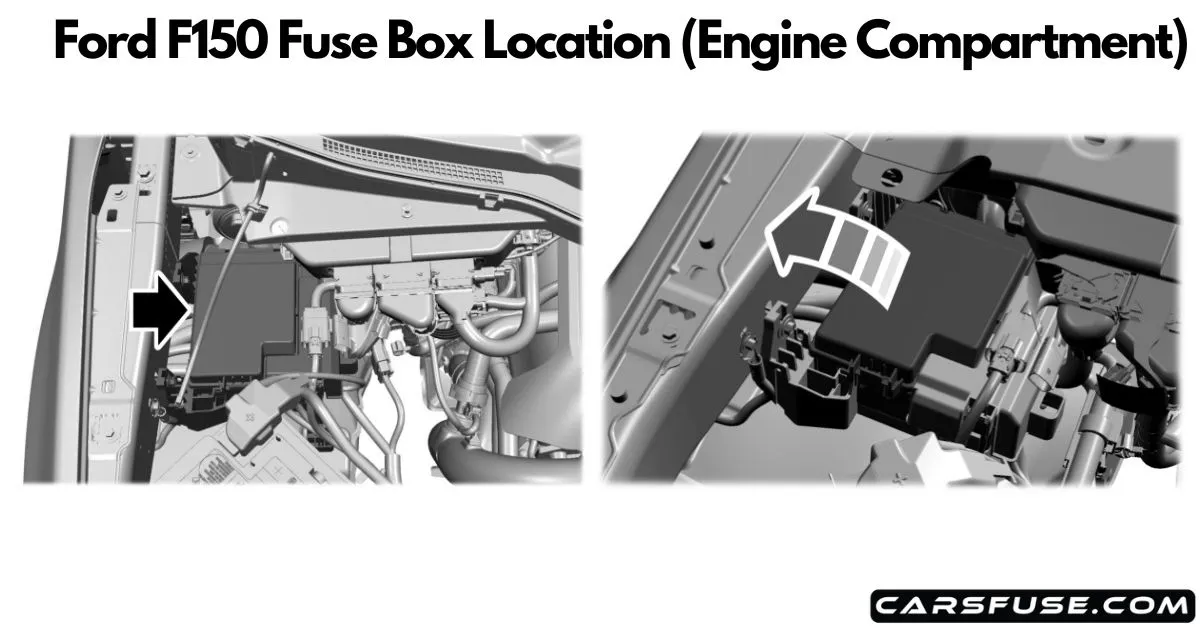
Depending on the year of your F-150, you’ll generally find two or three fuse boxes:
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Box (Interior Fuse Panel) – Usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Power Distribution Box (Engine Bay) – Found in the engine compartment near the battery.
- Optional Auxiliary Fuse Box (for Towing/Upfits) – Present in some newer or heavy-duty models, often mounted near the front of the engine bay.
Each box houses multiple fuses and relays with unique numbers and ratings.
Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams by Year
Below is a general breakdown of fuse box locations and layouts for different generations.
Ford F-150 (2021–2023)

The latest F-150 models feature advanced electrical systems, including hybrid and EV variants.
- Under Hood Fuse Box: Mounted on the passenger side near the battery.
- Body Control Module Fuse Box: Located under the steering column, above the brake pedal.
Common fuses include: - Fuse #10 – Power outlet
- Fuse #24 – Fuel pump
- Fuse #33 – Headlamps
- Fuse #56 – A/C compressor clutch
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 2021-2023 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Tip: Hybrid F-150 models may include additional fuses for the high-voltage battery system.
Ford F-150 (2015–2020)

The aluminum-body generation introduced a redesigned electrical system with multiple smart relays.
- Under Hood Fuse Box: Next to the battery on the driver’s side.
- Body Control Module Fuse Box: Under the right-hand side of the instrument panel.
Key fuses: - Fuse #12 – Trailer tow
- Fuse #15 – Power windows
- Fuse #18 – PCM (Powertrain Control Module)
- Fuse #40 – Horn
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 2015-2020 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Ford F-150 (2009–2014)
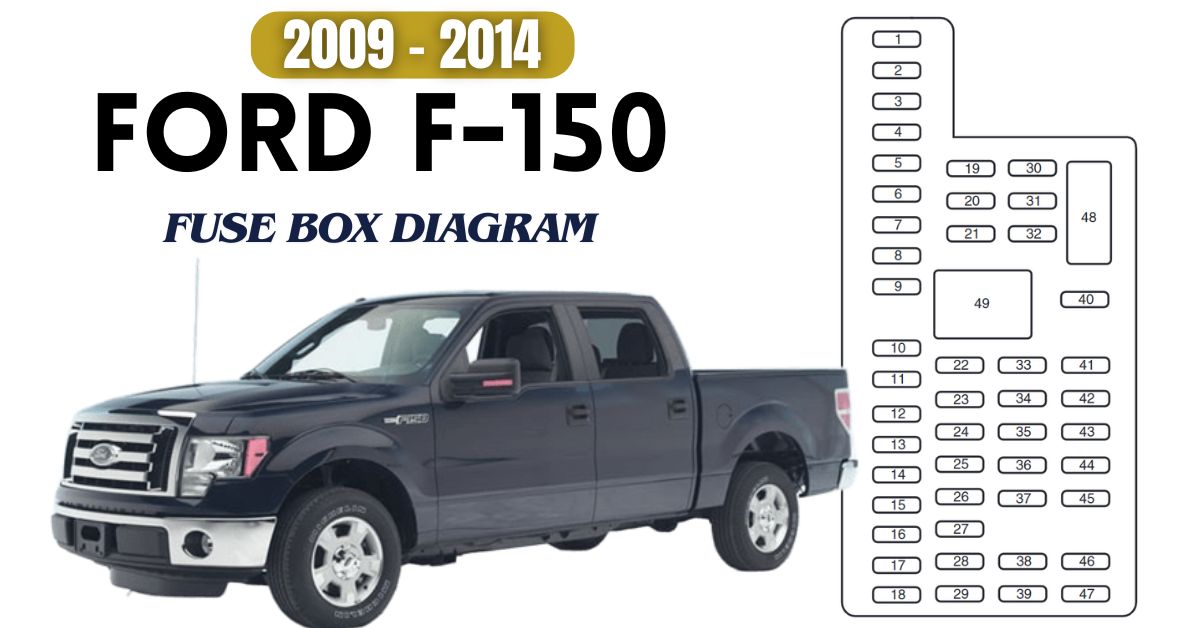
These models feature two primary fuse boxes.
- Passenger Compartment: Behind the passenger-side kick panel.
- Power Distribution Box: Next to the battery.
Common fuses: - Fuse #9 – Wiper motor
- Fuse #22 – A/C system
- Fuse #34 – Radio
- Fuse #47 – Headlamp relay
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 2009-2014 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Ford F-150 (2004–2008)
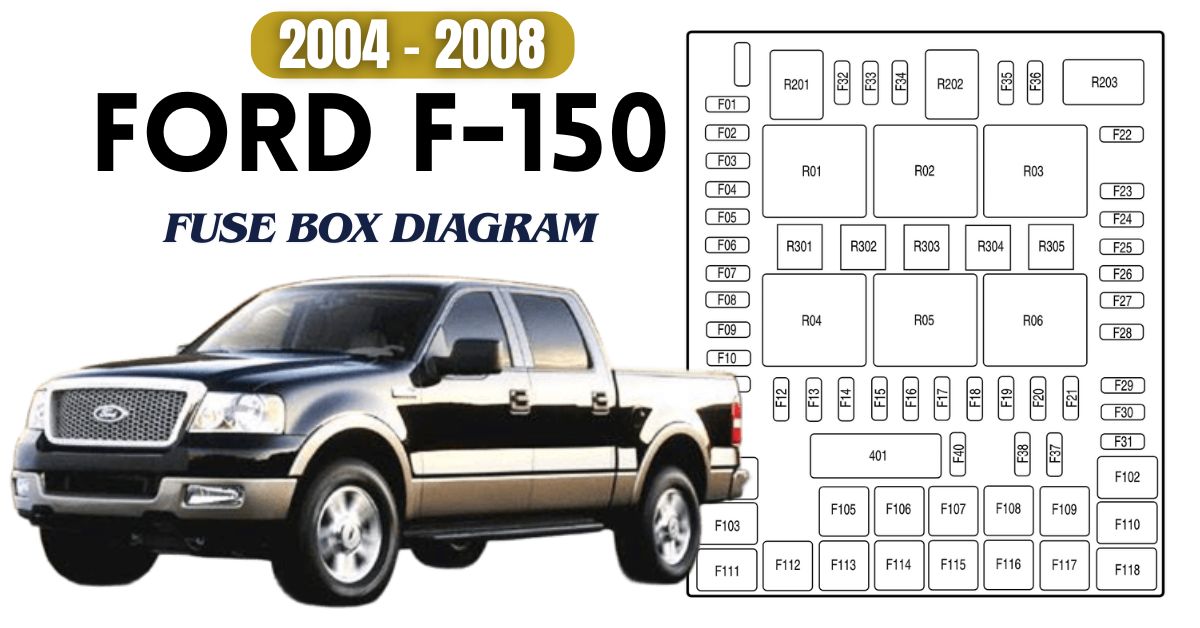
- Interior Fuse Box: Under the steering wheel.
- Engine Fuse Box: Near the battery on the driver’s side.
Frequent issues include: - Blown fuse for cigarette lighter (Fuse #41)
- ABS light on due to blown Fuse #102
- Power window malfunction (Fuse #12)
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 2004-2008 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Ford F-150 (1997–2003)
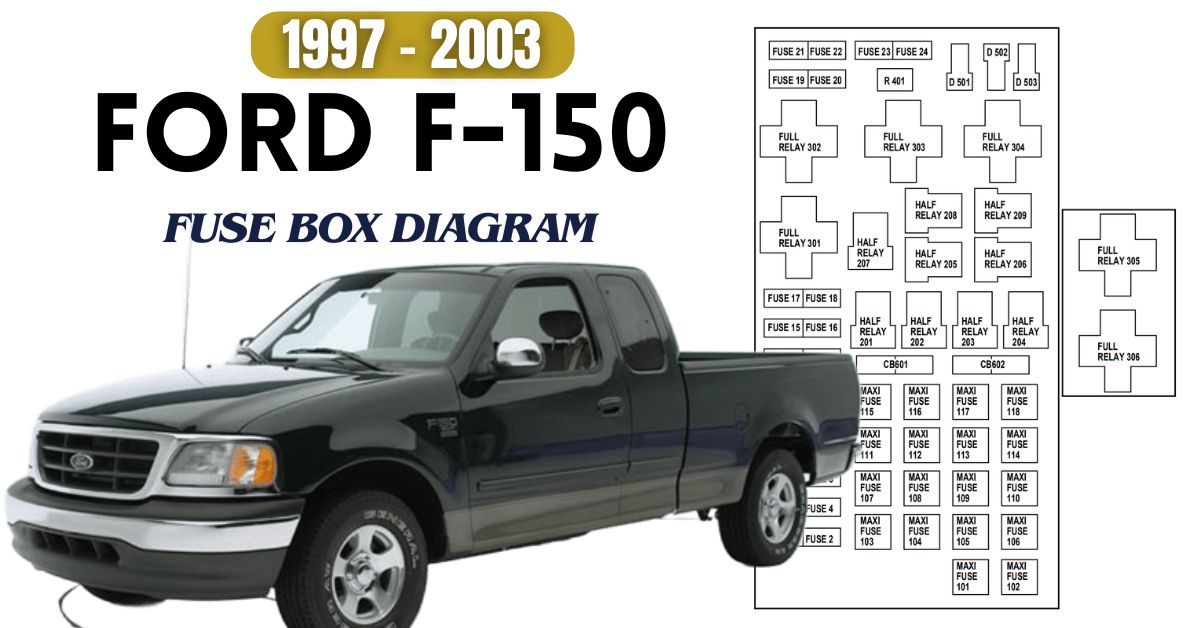
This generation includes two fuse panels: one inside the cabin, another under the hood.
- Fuse #1 – Stop lamps
- Fuse #5 – Instrument cluster
- Fuse #15 – Fuel pump relay
- Fuse #20 – Horn
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 1997-2003 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Ford F-150 (1992–1996)

Older F-150s used simpler electrical setups, but fuse placement remains similar.
- Fuse Box: Under the dash, left of the steering column.
Key functions: - Fuse #5 – Headlights
- Fuse #9 – Heater blower motor
- Fuse #12 – Ignition coil
- Fuse #15 – Radio
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 1992-1996 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Ford F-150 (1987–1991)

These classic F-150s feature a basic fuse block under the dashboard.
- Fuse #1 – Turn signals
- Fuse #3 – Brake lights
- Fuse #5 – Instrument panel
- Fuse #9 – Wipers
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 1987-1991 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Note: Over time, corrosion or loose contacts in older fuse panels can cause intermittent power failures. Always inspect terminals for rust or oxidation before replacing fuses.
Ford F-150 (1985-1986)

These classic F-150s feature a basic fuse block under the dashboard.
- Fuse #1 – Turn signals
- Fuse #3 – Brake lights
- Fuse #5 – Instrument panel
- Fuse #9 – Wipers
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 1985-1986 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagrams
Note: Over time, corrosion or loose contacts in older fuse panels can cause intermittent power failures. Always inspect terminals for rust or oxidation before replacing fuses.
Ford F-150 (1980)

These classic F-150s feature a basic fuse block under the dashboard.
- Fuse #1 – Turn signals
- Fuse #3 – Brake lights
- Fuse #5 – Instrument panel
- Fuse #9 – Wipers
For Complete Fuse Box Diagrams, Visit Here: 1980 Ford F-150 Fuse Box Diagram
Note: Over time, corrosion or loose contacts in older fuse panels can cause intermittent power failures. Always inspect terminals for rust or oxidation before replacing fuses.
4. How to Check or Replace a Fuse
- Turn off your ignition and remove the key.
- Locate the proper fuse using the diagram on the fuse box cover or owner’s manual.
- Use a fuse puller or tweezers to gently remove the fuse.
- Check if the metal strip inside is broken — if yes, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Reinstall the fuse and test the system.
Caution: Never replace a fuse with one rated higher than specified — it can lead to serious electrical damage or fire.
5. Common Ford F-150 Fuse Problems
The fuse box in your Ford F-150 plays a crucial role in protecting the vehicle’s electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. However, like any electrical component, it can develop issues over time that may lead to partial or complete electrical failure. Understanding the most common fuse box problems and their underlying causes will help you diagnose and fix them effectively before they cause bigger electrical damage.
Below are the most frequent fuse box problems seen in Ford F-150 trucks — across various generations — and the reasons behind them.
| Problem | Common Symptoms | Likely Causes | Quick Fix / Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Blown Fuse | One or more components (headlights, radio, horn, A/C, etc.) suddenly stop working. | Short circuit, overloaded circuit, or faulty accessory. | Locate and replace the fuse with the correct amp rating. Check wiring and devices connected to that circuit. |
| 2. Melted or Burnt Fuse Terminals | Burnt smell, melted plastic, or blackened terminals inside the fuse box. | Loose fuse connection, corrosion, or high current draw. | Clean or replace the fuse box terminal. Ensure fuse fits tightly. Inspect for heat damage or burnt wires. |
| 3. Corroded Fuse Box or Connectors | Flickering lights, intermittent power loss, green or white residue on fuses. | Water leak, poor sealing, or exposure to road salt and moisture. | Disconnect battery, clean terminals with electrical cleaner, apply dielectric grease, and seal openings against water. |
| 4. Loose or Faulty Relays | Engine won’t start, A/C or fuel pump cuts off, or clicking noise from fuse box. | Worn relay contacts, vibration, or heat damage. | Reseat or replace faulty relays. Clean contacts and ensure relays are fully inserted. |
| 5. Water or Moisture Intrusion | Random warning lights, damp fuse box, rusted contacts, electrical shorting. | Leaking windshield or hood seals, poor drainage, off-road water exposure. | Dry the area, clean corrosion, and reseal leaks. Replace any rusted connectors or affected fuses. |
| 6. Faulty Power Distribution Box (PDB) | Multiple systems fail at once, truck won’t start, battery drain. | Cracked solder joints, manufacturing defect, or overload from aftermarket accessories. | Replace the PDB if internal failure is confirmed. Ensure all wiring and grounds are secure. |
| 7. Ignition or PCM Fuse Blowing Repeatedly | Engine won’t crank or start, check engine light, no OBD communication. | Shorted wiring, faulty sensor, or poorly installed aftermarket electronics. | Inspect and repair wiring harness. Remove aftermarket devices temporarily to isolate the fault. Replace PCM fuse once issue is resolved. |
| 8. Fuse Box Overheating | Fuse box feels hot, burnt odor, melted casing, or random electrical cutouts. | Excessive electrical load, poor ground, or aging components. | Reduce accessory usage, check all grounds, and replace any discolored fuses or connectors. Ensure ventilation around fuse box. |
1. Blown Fuses
Description:
One of the most common issues in the F-150 fuse system is a blown fuse. It usually results in a single electrical function, like the headlights, horn, radio, or power windows, suddenly stopping.
Possible Reasons:
- Short Circuit: A wire touching metal or another live wire can cause excess current flow.
- Overloaded Circuit: Using high-power accessories such as aftermarket lights or stereos without proper wiring.
- Faulty Component: A malfunctioning device (like a failing motor or sensor) can draw too much current.
- Water Intrusion: Especially in models from 2015 onward, moisture in the fuse box can cause shorting.
Affected Models:
Common in all model years, especially 2004–2008 and 2015–2020 F-150 trucks.
2. Melted or Burnt Fuse Terminals
Description:
Some owners notice melted plastic or burnt marks on fuse terminals. This is a sign of overheating due to poor electrical contact.
Possible Reasons:
- Loose Fuse Connection: If a fuse is not seated firmly, it can cause resistance and heat buildup.
- Corrosion on Contacts: Moisture, road salt, or battery acid vapors can oxidize the contacts, creating poor conductivity.
- High Current Draw: Accessories pulling more current than the fuse circuit is designed for.
Affected Models:
Mostly found in 1997–2003 and 2009–2014 F-150 models, particularly around high-load circuits like the blower motor and trailer wiring.
3. Corroded Fuse Box or Connectors
Description:
Corrosion inside or around the fuse box can disrupt current flow and cause intermittent power loss to critical systems like the headlights or ignition.
Possible Reasons:
- Water Leak: From the windshield, cowl panel, or hood seals dripping onto the fuse box.
- Poor Drainage Design: Engine bay fuse boxes in older F-150s often accumulate condensation.
- Road Salt and Moisture Exposure: Especially in regions with heavy winters or humidity.
Symptoms:
- Random electrical failures
- Flickering headlights or dashboard lights
- Fuse terminals covered in green or white residue
Affected Models:
Most common in 1997–2008 F-150s due to weather sealing limitations.
4. Loose or Faulty Relays
Description:
A relay is an electrical switch that controls high-current circuits such as the fuel pump, cooling fan, or A/C compressor. A loose or faulty relay in the fuse box can mimic a blown fuse problem.
Possible Reasons:
- Vibration and Age: Continuous vibration from driving can loosen relay connections.
- Worn Relay Contacts: Over time, the metal points inside relays can pit and corrode.
- Heat Exposure: Constant heat from the engine bay degrades the internal components.
Symptoms:
- Intermittent starting issues
- A/C or fuel pump suddenly stopping
- Clicking noises from the fuse box area
Affected Models:
Primarily 2009–2014 and 2015–2020 Ford F-150s.
5. Water or Moisture Intrusion in Fuse Box
Description:
Water intrusion is one of the most serious and recurring fuse box issues in modern F-150s. It can cause electrical shorts, corrosion, and even total power loss.
Possible Reasons:
- Leaking Windshield Seal or Cowl Panel: Water seeps through and drips directly into the interior fuse panel.
- Damaged Hood Seals: Allow rainwater to reach the under-hood fuse box.
- Off-Road Conditions: Mud, rain, or pressure washing forcing water into the housing.
Symptoms:
- Random warning lights
- Electrical components failing intermittently
- Damp or rusty fuse terminals
- Burning smell or clicking from fuse box area
Affected Models:
Common in 2015–2020 and 2021–present models, including hybrid versions.
6. Faulty Power Distribution Box (PDB)
Description:
The Power Distribution Box (engine compartment fuse box) is responsible for handling high-current circuits. Internal faults here can cause complete power failure to certain systems.
Possible Reasons:
- Cracked Solder Joints or Internal Damage: From vibration or overheating.
- Manufacturing Defect: Rare, but reported in certain production years.
- Aftermarket Modifications: Poor installation of accessories like LED bars or winches can overload or damage the PDB.
Symptoms:
- No crank or no-start condition
- Multiple electrical systems failing simultaneously
- Battery drain even when ignition is off
Affected Models:
Frequently reported in 2004–2008 and 2009–2014 trucks.
7. Ignition Circuit or PCM Fuse Blowing Repeatedly
Description:
When the fuse related to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or ignition keeps blowing, it indicates a more serious electrical fault in the engine control system.
Possible Reasons:
- Shorted Sensor or Wiring Harness: Common with oxygen sensors or injector wiring.
- Moisture in PCM Connectors: Especially in older trucks or those exposed to heavy rain.
- Faulty Aftermarket Device: Remote start, alarm, or tuning devices improperly wired to ignition circuits.
Symptoms:
- Engine won’t start
- Check Engine Light illuminated
- No communication with PCM via OBD-II scanner
Affected Models:
Mostly 1997–2003 and 2009–2014 F-150s.
8. Fuse Box Overheating
Description:
A hot fuse box or burnt smell near it suggests excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
Possible Reasons:
- High Electrical Load: Too many accessories running simultaneously.
- Aging Components: Heat cycles weaken internal plastic and terminals.
- Poor Ground Connection: Causes voltage spikes and current surges.
Symptoms:
- Melted fuse box plastic
- Intermittent electrical failure
- Burning odor under dash or hood
Affected Models:
Can occur in any generation, particularly high-mileage or heavily accessorized F-150s.
How to Prevent Fuse Box Problems
- Keep the fuse box area clean and dry.
- Regularly check for loose or corroded terminals.
- Avoid overloading circuits with aftermarket accessories.
- Replace fuses and relays only with OEM-rated components.
- If you notice repeated fuse failures, have the circuit diagnosed by a professional — replacing fuses repeatedly without finding the cause can worsen damage.